Abstract
Laboratory automation using experimental robots is expected to be a technology that will solve problems such as labor-intensive operation of laboratories,
hazardous experimental work, humanized and tacit knowledge of experimental techniques, low reproducibility, and research fraud.
However, current experimental robots are specialized for specific experimental tasks and cannot replace various experimental tasks performed by humans,
and they lack flexibility because the positions of all experimental apparatuses must be decided in advance.
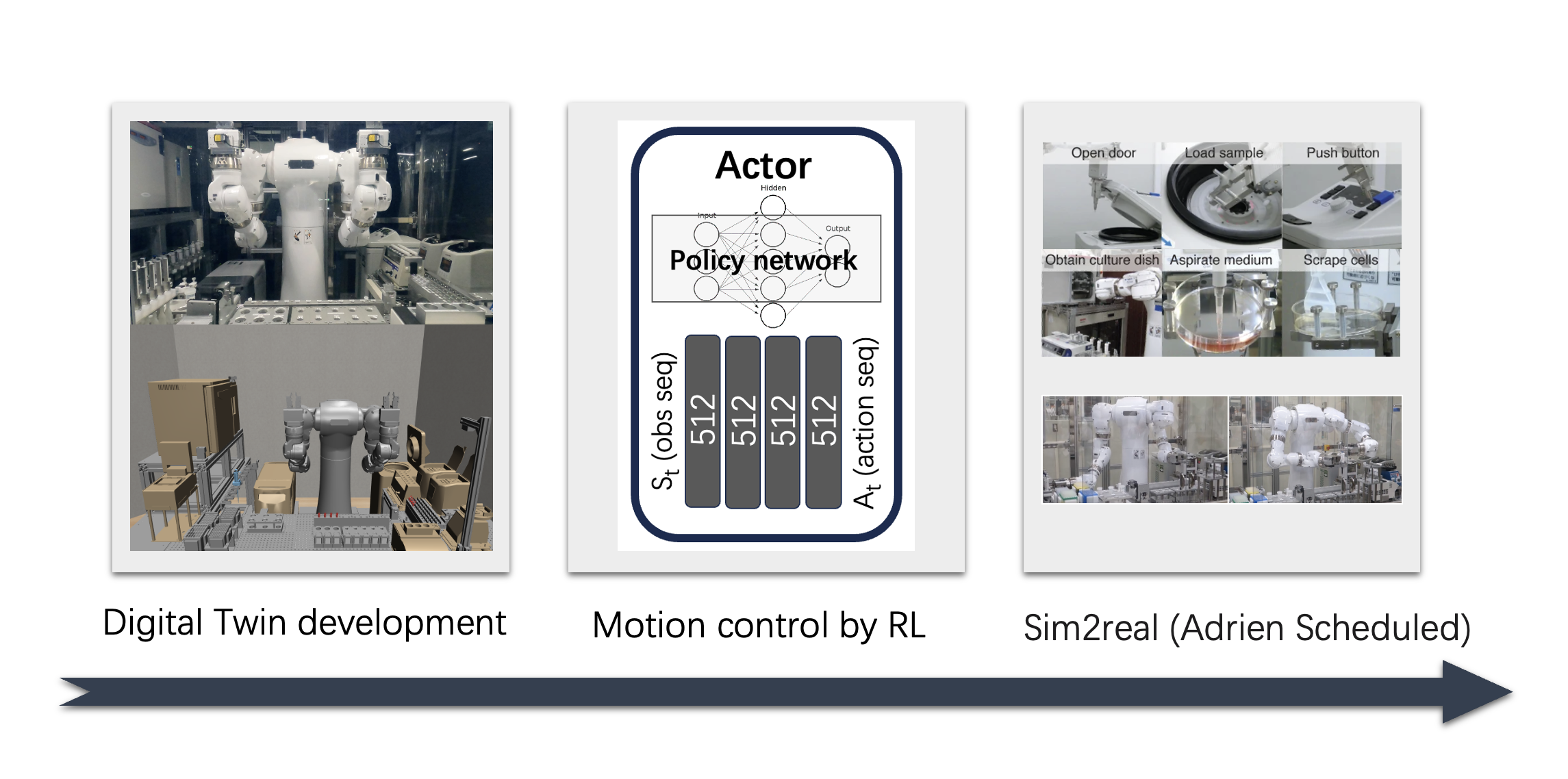
In this study, we propose a new approach in which a virtual laboratory (digital twin) built on a computer is used to learn AI so that the robot can flexibly perform various experimental tasks,
and the motion data is then transferred to the actual robot. Using the highly versatile dual-armed experimental robot Maholo as a subject, we show an example of learning behaviors of Maholo built on a simulator.
This research is expected to improve the efficiency of motion learning of experimental robots and realize more complete laboratory automation.
Keywords
Laboratory automation, Autonomous experimental robot, Maholo, Digital twin